Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells are photovoltaic devices formed by sequentially depositing multiple layers of semiconductor thin films on a glass substrate.
Structure
Standard cadmium telluride power-generating glass consists of five layers, namely the glass substrate, the TCO layer (transparent conductive oxide layer), the CdS layer (cadmium sulfide layer, serving as the window layer), the CdTe layer (cadmium telluride layer, acting as the absorption layer), the back contact layer, and the back electrode.

Performance Advantages
High photoelectric conversion efficiency: Cadmium telluride cells have a relatively high ultimate conversion efficiency of approximately 32% - 33%. Currently, the world record for the photoelectric conversion efficiency of small-area cadmium telluride cells is 22.1%, and the module efficiency is 19%. Moreover, there is still room for improvement.
Strong light absorption ability: Cadmium telluride is a direct bandgap semiconductor material with a light absorption coefficient greater than 105/cm, which is approximately 100 times higher than that of silicon materials. A cadmium telluride thin film with a thickness of only 2μm has an optical absorption rate exceeding 90% under standard AM1.5 conditions.
Low temperature coefficient: The bandgap width of cadmium telluride is higher than that of crystalline silicon, and its temperature coefficient is approximately half that of crystalline silicon. In a high-temperature environment, for example, when the module temperature exceeds 65°C in summer, the power loss caused by the temperature increase in cadmium telluride modules is approximately 10% less than that in crystalline silicon modules, making its performance better in high-temperature environments.
Good performance in generating electricity under low light conditions: Its spectral response matches the ground solar spectral distribution very well, and it has a significant power generation effect under low light conditions such as in the early morning, at dusk, when dusty, or during haze.
Small hot spot effect: Cadmium telluride thin-film modules adopt a long-strip sub-cell design, which helps reduce the hot spot effect and improves the product's lifespan, safety, stability, and reliability.
High customizability: It can be applied to different building application scenarios and can flexibly customize colors, patterns, shapes, sizes, light transmittance, etc., to meet the power generation needs of buildings from multiple perspectives.

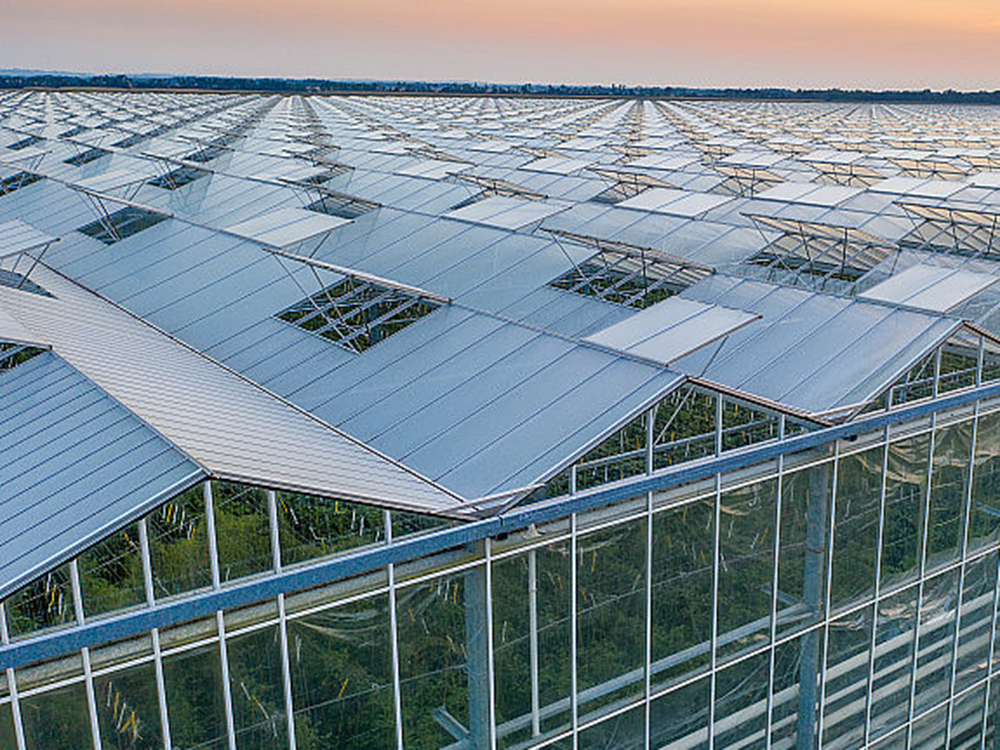
Advantages in Application to Greenhouses
The cadmium telluride glass greenhouse can adjust the light transmittance and spectral characteristics according to the light requirements of different crops.
In summer when the temperature is high, the cadmium telluride glass can play a sunshade role by adjusting the light transmittance and reflectivity, reducing the solar radiation heat entering the greenhouse and lowering the temperature inside the greenhouse. In winter or on cold nights, it can also reduce heat loss and play a heat preservation role. Coupled with the electricity generated, it can supply power to heating equipment to create a suitable growth temperature environment for plants.
Cadmium telluride glass has relatively good strength and durability and can withstand certain natural disasters and external impacts, such as wind, rain, and hail, providing a more stable and safe growth environment for the crops inside the greenhouse. At the same time, it also reduces the maintenance and replacement costs of the greenhouse.

Post time: Dec-02-2024

